“I plan to retire at age 57 with an MRA + 10 option. I don’t plan on taking my FERS retirement out until later age 61 or 62 depending. I have the basic life insurance and single. What is the best option to defer retirement or postpone retirement?” – Floyd.
As a federal employee, you can retire from federal service and receive a lifetime pension if you meet the qualifications.
What some federal employees don’t realize is that there are different types of retirement that they might be eligible to apply for:
There are various types of FERS retirement:
- Immediate retirement: This is the most common type of retirement. You can retire immediately if you have at least 30 years of creditable service or are 62 or older with at least 5 years of creditable service.
- Early retirement: Reduced retirement under MRA + 10.
- Postponed retirement: Postponed retirement is a type of retirement under the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) that allows you to delay the start of your retirement benefits.
- Deferred retirement: You can defer retirement until any age after you reach your MRA (Minimum Retirement Age). Your benefit will be increased for each year you defer retirement.
- Disability retirement: You can retire on disability if you cannot perform the duties of your position due to a physical or mental disability. You must meet certain requirements to be eligible for disability retirement.
Most federal employees apply for Immediate Retirement, but other types of retirement can be considered contingent on several factors.
Let’s walk through the various types of retirement for Federal Employees.
Understanding federal employees’ various types of retirements is critical to their long-term financial success.
Choosing the wrong one could cost you your health benefits for the rest of your life.

Immediate Retirement
To be eligible for immediate retirement under the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS), you must meet one of the following requirements:
- You must have at least 30 years of creditable service.
- You must be at least age 62 with at least 5 years of creditable service.
- If you meet one of these requirements, you can retire immediately and begin receiving your FERS retirement benefit. Your benefit will be based on your years of creditable service, your age at retirement, and your highest three consecutive years of pay.
If you retire before age 62, your benefit will be reduced. The amount of the reduction is based on your age at retirement. For example, if you retire at age 60, your benefit will be reduced by 5%.
You can use the FERS Retirement Estimator to calculate your estimated retirement benefit.
But what happens if you, like Floyd, do not want to apply for an immediate retirement? What are your options to retire from Federal Service?
Early Retirement “MRA+10”
You can retire from Federal Service when you have reached your minimum retirement age and have 10 years of service.
Retiring under an MRA+10 Retirement will give you a permanent lifetime reduced pension.
Your pension will be reduced if you retire before age 62.
The reduction equals five percent per year (or 5/12 of one percent per month) for each year you are under age 62.
To avoid the reduction, you can postpone payment.
You can later apply for the benefit by writing to us or filing an “Application for Deferred or Postponed Retirement,” Form RI 92-19.
MRA+10 (MRAandten)
MRA10 retirement is a retirement option under the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) that allows you to retire with a reduced pension after you have reached your Minimum Retirement Age (MRA) and have at least 10 years of creditable service.
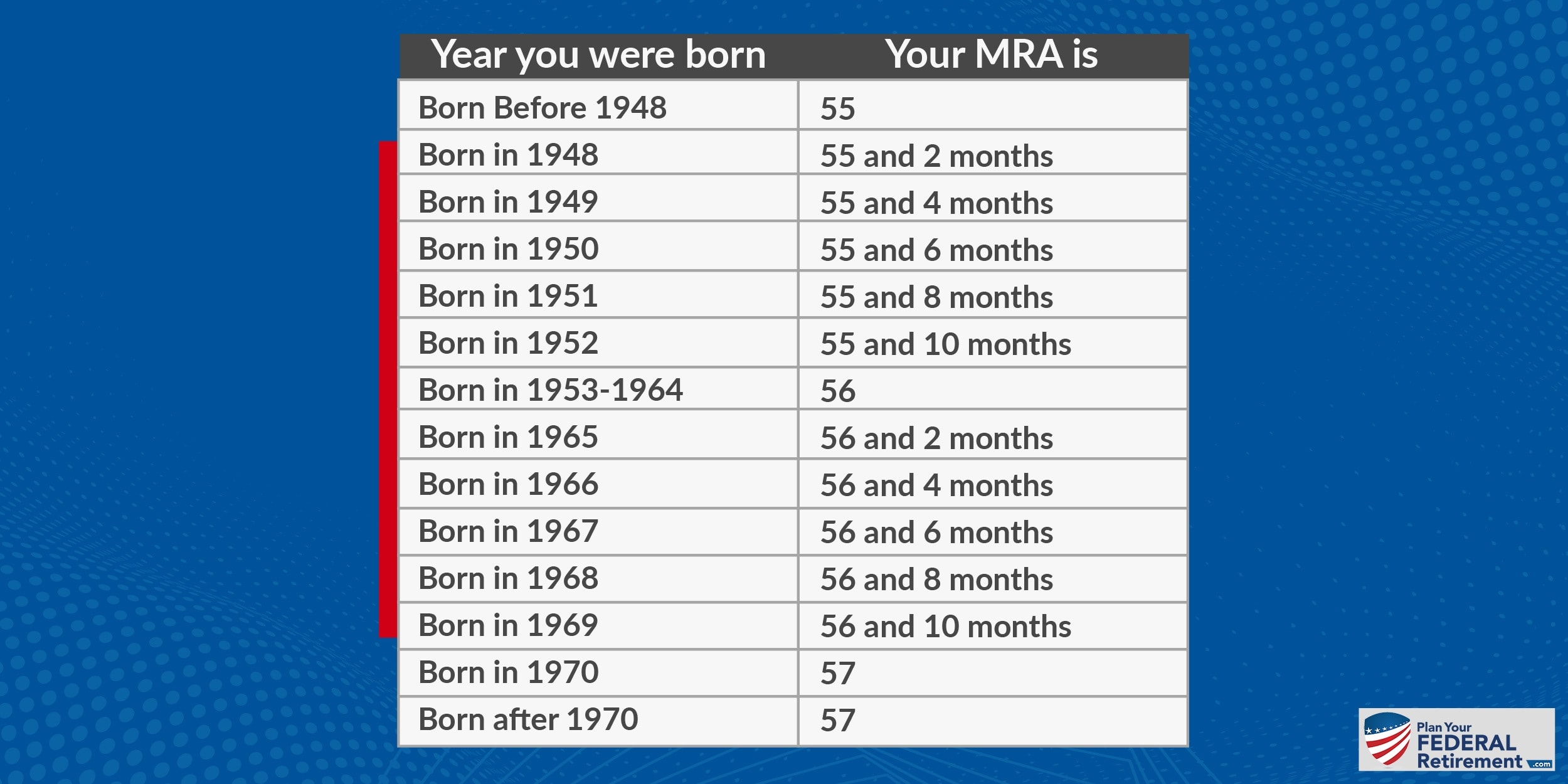
Your MRA is based on your birth year.
If you retire under MRA10, your pension will be reduced by 5% for each year you are under age 62. For example, if you retire at age 57 with 10 years of service, your pension will be reduced by 25%.
Whether or not you should elect to retire under an MRA10 rule depends on your cash flow and long-term retirement plan.
If you need to retire and start taking a pension NOW, then maybe paying the price for the reduction each year is worth considering.
However, if you have time in federal service and can financially plan to delay taking retirement benefits until you have met your retirement qualifications under a Postponed Retirement, it is something you should consider seeing if it is right for you.
Postponed Retirement
Postponed retirement is a type of retirement under the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) that allows you to delay the start of your retirement benefits – you are stopping federal service, placing your benefits on a shelf, and postponing applying for retirement.
When you reach your retirement age, assuming you meet the other qualifications for immediate retirement, you can apply for retirement. Under a postponement, you can apply for retirement ant turn your benefits “back on.” Benefits like your insurance coverage.
This can be a good option if you want to continue working and earning a salary in the private sector.
To be eligible for postponed retirement, you must meet the following requirements:
- You must have at least 10 years of creditable service.
- You must have reached your Minimum Retirement Age (MRA).
- If you meet these requirements, you can choose to postpone the start of your retirement benefits until any later date. For each year that you postpone retirement, your retirement benefit will increase by 1%.
For example, if you have 20 years of creditable service and reach your MRA at age 60, you can postpone retirement until age 62.
There are a few things to keep in mind when considering postponed retirement:
You will continue to be eligible for health insurance and other benefits through your federal employment.
You will continue to earn a salary, which can help you save for retirement or pay for other expenses.
You will not be subject to an early retirement reduction if you retire after age 62.
If you are considering postponed retirement, you should talk to a federal benefits specialist to determine which option is right for you.
Deferred Retirement – PROCEED WITH CAUTION
Deferred retirements are not bad. You just have to understand the rules.

You can defer retirement until any age after you reach your MRA (Minimum Retirement Age). Your benefit will be increased for each year you defer retirement.
Deferred retirement is a type of retirement under the Federal Employees Retirement System (FERS) that allows you to retire after reaching your Minimum Retirement Age (MRA), but before you are eligible for an immediate annuity. This can be a good option if you want to continue working and earning a salary or if you want to increase the size of your retirement benefit.
To be eligible for deferred retirement, you must meet the following requirements:
- 10 years of creditable service at the minimum.
- Reach your Minimum Retirement Age (MRA)
- If you meet these requirements, you can choose to defer retirement until any later date. Each year you defer retirement, your retirement benefit will increase by 1%.
For example, if you have 20 years of creditable service and reach your MRA at age 60, you can choose to defer retirement until age 62. Your retirement benefit will be increased by 20% (2 years x 1%).
Ready to talk with a federal employee benefits specialist?

